WHAT WE HAVE ON THIS PAGE
Introduction
Urban Farming Statistics: Urban farming is when someone living in a crowded city or town takes over their area to plant food or keep small animals. Not all urban farms have to be located at the farm owners’ home or farm. Some urban farmers can lease their land and use the soil of other homeowners’ backyards, as well as the rooftops of indoor or outdoor farms.
Much like a garden at home, urban farmers grow to feed the populace, often selling their produce for little or no gain. Urban farming is designed to improve accessibility to fresh and local foods. Many urban farms are located on the balcony or in the garden. They can grow vegetables, collect eggs, and cut chicken meat. In the following article, we will look at the statistics of urban farming.
Editor’s Choice
- Almost 51% of the households grow vegetables and fruits, which contributes to notable urban agriculture in Toronto.
- The urban agriculture in Philadelphia extends almost 470 acres of land.
- Nearly 96% of the city’s greens are generated from urban and peri-urban agriculture in Tokyo, Japan.
- Over 200,000 people can be fed enough goods grown by the urban farmers in Los Angeles, California.
- Detroit holds almost 1,400 urban farms and community gardens.
- Urban farming is predicted to cover almost 100 acres of land in New York City.
- The average urban farmer in Africa is between 35 years and 64 years old.
- The global indoor farming market was valued at USD 33.9 billion in 2022.
- It is projected to reach USD 93.0 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 10.9%.
- In Havana, Cuba, almost 27% of food is consumed from urban farming within the city limits.
- Ohio has invested in urban agriculture, which could supply 46% to 100% of Cleveland’s fresh produce needs.
- Urban agriculture supplies up to 90% of the cities in developing urban countries with fresh fruits and vegetables.
- As a result of urban agriculture, the chances of job positions increase by 4.1% within eight years.
- As per urban farming statistics, in the United States, there are almost 29,000 urban farms.
- Nearly 70% of the farmers cultivate fruits and vegetables for their private consumption and also for their family and friends.
- By 2023 the global urban farming market is projected to be valued at $160.8 billion.
- Urban agriculture has the power to provide almost 10% of worldwide vegetable production.
- In the forecasted period 2021 – 2026, the urban agricultural market size was projected at $213 billion in 2020 at a CAGR of 2.8%.
You May Also Like To Read
Urban Farming Key Facts
- Detroit is famous for urban agriculture because urban agriculture modification has been an effective tool for improving neighbourhood quality, increasing social skills, and decreasing problems like crimes and urban land vacancy.
- The Michigan urban agriculture is an initiative taken by the state of Michigan in the US to promote urban agriculture programs and get the benefits that those
- Urban agriculture is still a growing movement, and some sites concentrate on urban farming and related topics.
- Garden plots can be 20 times more productive than rural holdings.
- The producers that act as middlemen in urban farming are consumed either by the producer or sold at a local market by the producer.
- The Urban Farming Guys (UFG) has gained noteworthy popularity and press coverage and currently has almost 11,000 Facebook followers.
- Curtis Stone is a famous urban agriculture leader who developed a system that allowed him to earn a profit of almost $100k from agriculture alone.
- The food grown in the backyard means less transportation and cooling costs and emissions, which is good news for the atmosphere, but that shall almost make food grown in the urban agricultural fields more comparable.
- According to urban farming statistics, Curtis’s YouTube channel has a huge amount of content related to the business and techniques used for urban agriculture, and it has gained almost 325,000 followers.
- Over the last ten years, Chicago has experienced a growth in commercial and social impact focusing on urban farms.
- Urban agriculture has increased in Los Angeles in the last couple of years. As a result, the southern California weather is suitable for the crops in any type of urban farm design.
- The Growing Power in Milwaukee, USA, was founded by Will Allen, who was a professional basketball player.
- Urban farms provide food to almost 700 million cities, which is one-fourth of the world’s urban population.
- Urban farming is also organic, which means that the production is healthier than that of products grown on large-scale farms that use pesticides.
- Hunger is still a major issue even in developed countries, so urban farming provides an inexpensive source of nutritious food, with agricultural plots managed by communities.
- Urban farming generally produces a more diverse set of crops, while urban gardeners tend to grow fewer crops and plants that promote agricultural diversity.
- Urban farming generates less food waste as the food from the urban farms reaches the final consumers fast and thus lasts longer and has been frequently purchased.
- The plants also absorb carbon dioxide, which helps to fight climate change, and the green spaces have reduced air pollution.
- Urban agriculture involves more than just planting or vegetation; it also involves animal husbandry, aquaculture, agroforestry, and horticulture.
Indoor Agricultural Market Forecast
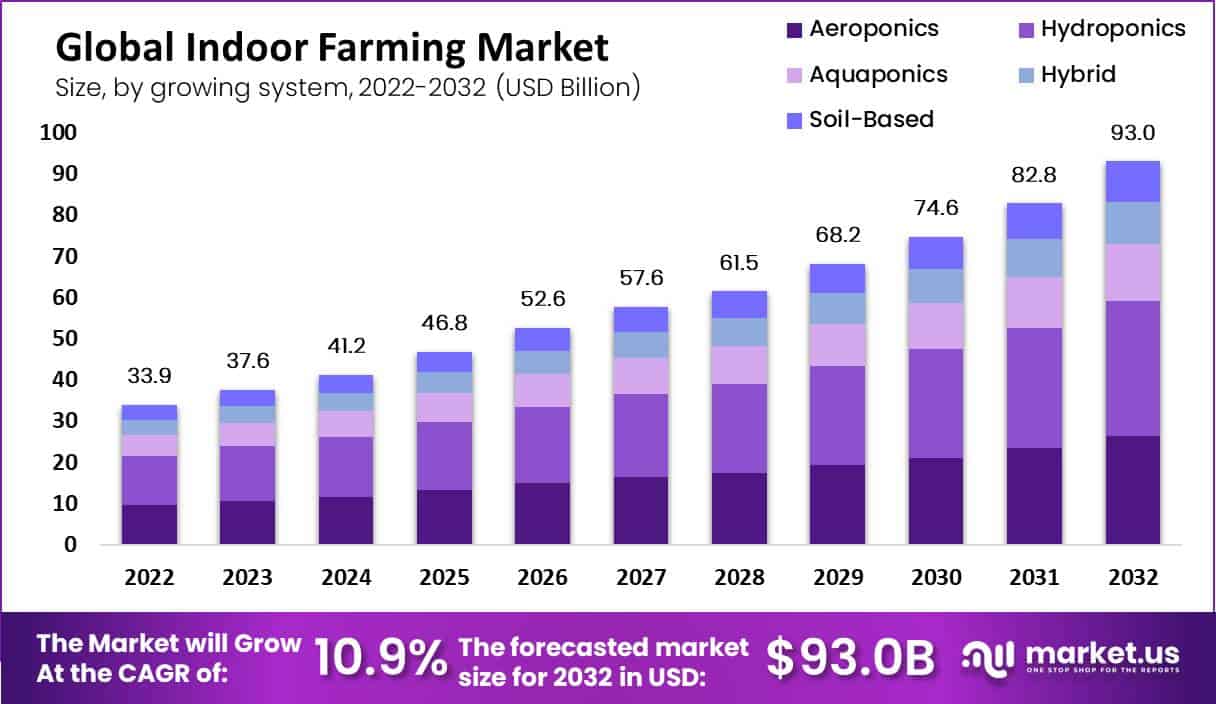
- The global indoor farming market was valued at USD 33.9 billion in 2022.
- It is projected to reach USD 93.0 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 10.9%.
- Vertical farming, where crops are grown in stacked layers, is a prominent method of indoor farming.
- Hydroponics, a method of growing plants without soil, dominated the market in 2022.
- Indoor vertical farming is expected to grow the fastest due to increased demand for eco-friendly produce.
- The hardware segment, including sensors and climate control systems, is set to dominate the market.
- Fruits and vegetables, particularly tomatoes, are the leading crop types in indoor farming.
- Drivers include rising demand for fresh, locally grown produce and advancements in technology.
- Challenges include high initial investment costs and energy consumption concerns.
- Europe held the largest market share in 2022, driven by the adoption of controlled-environment agriculture.
- Asia Pacific is expected to grow fastest, led by countries like Japan and China.
- LED lighting and AI technologies are transforming indoor farming practices.
- Sustainability efforts include using renewable energy sources and recycling wastewater.
- The greenhouse segment remains dominant for facility types in indoor farming.
- North America and Europe are key regions due to technological advancements.
- Key players include Argus Control Systems, Signify Holding, and LumiGrow.
Factory Farming Statistics
- In the United States, factory farms produce almost 130 times as much waste as the entire human population.
- The factory farms use enough water daily to fill 4,200 Olympic-sized swimming pools.
- Nearly 80% of the farmland is used to rear the 60 billion domestic animals in the factory farms thus producing just 18% of the world’s calories.
- More than 30% of the loss in biodiversity is the result of factory farming globally.
- According to urban farming statistics, a cow produces almost 1000 liters to 3000 liters of ammonia in manure while on a factory farm for her entire life.
- In the United States, factory farms account for nearly 10 billion land animals per year.
- Virtually 50% of the fish production globally comes from factory farms.
- Nearly 90% of the pigs are raised on factory farms in the European Union.
- Factory farms are responsible for almost 33 million metric tons of food waste in the United States each year.
- Practically 30% are injured sometime during their work years annually in factory farms in the United States.
- Nearly 95% of the broiler chickens are raised on the factory farms in the UK.
- Factory farms produce 14.5% of the total greenhouse gas emissions worldwide, more than the transport sector.
- Almost 99% of the farmed animals are raised in factory farms in the United States.
- Factory farming accounts for almost 70% of all farmed animals globally.
- In the United States only, factory farms and houses are worth 9 billion animals.
- The factory farming industry consumes around 80% of the global supply of soy.
- Virtually 80% of the antibiotics sold in the US are used in farm animals.
- Annually, factory farms produce almost 500 million tons of animal manure in the United States.
- In 2020, the United States produced almost 70.4 billion pounds of poultry, 26.3 billion pounds of pork, and 24.1 billion pounds of beef.
- Factory farming emits almost 37% of methane and has more than 25 times the global warming potential of CO2.
Agriculture Improvement Act of 2018
- Urban farming initiatives received $40 million in federal funding to support the development and implementation of urban agricultural practices.
- The Environmental Quality Incentives Program allocated $20 million annually for urban agricultural projects aimed at improving soil quality and water conservation.
- Urban farms utilizing hydroponic systems have reported a 30% increase in crop yield compared to traditional soil farming.
- Over 50% of urban farms have adopted vertical farming techniques to maximize space efficiency and production.
- The average urban farm covers 2 acres of land, compared to traditional farms which average around 440 acres.
- Urban farms have been shown to reduce food transportation costs by up to 25%, contributing to lower carbon emissions.
- A survey indicated that 60% of urban farms use recycled materials for construction and maintenance of their infrastructure.
- Community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs in urban areas have grown by 15% annually, indicating increased local food consumption.
- The USDA’s Urban Agriculture and Innovative Production Program provided $10 million in grants to support urban farming education and research.
- Urban farming has been linked to a 20% increase in local food security in underserved communities.
- The number of urban farms in the United States has increased by 200% over the past decade.
- Approximately 70% of urban farms are involved in some form of direct-to-consumer sales, such as farmers’ markets or CSA programs.
- Urban farms have been found to use 80% less water than traditional farming methods due to advanced irrigation techniques.
- Studies show that urban farms can produce up to 8 times more food per square foot than traditional farms.
- Urban farming projects have created over 10,000 jobs in urban areas across the United States.
- On average, urban farms produce 30 different types of crops, contributing to greater biodiversity.
- Urban farms have reported a 50% reduction in food waste through efficient production and distribution methods.
- The USDA has established 10 regional offices to provide support and resources for urban farmers.
- Over 1,500 schools across the United States have integrated urban farming into their curriculum, impacting over 200,000 students.
- Urban farming has led to a 25% increase in green spaces in cities, contributing to better air quality and urban cooling.
- A study found that urban farming can reduce a city’s food desert area by up to 35%.
- The average urban farm produces 5,000 pounds of fresh produce per year.
- Urban farms have been shown to reduce stormwater runoff by 40%, helping to mitigate urban flooding.
- The number of urban farms participating in food assistance programs has increased by 50% in the past five years.
- Urban farms have contributed to a 20% reduction in urban heat islands through increased vegetation.
- The USDA’s Urban Agriculture Advisory Committee includes 12 members representing various urban farming stakeholders.
- Urban farms have been shown to improve community cohesion, with 70% of urban farmers reporting stronger community ties.
- The average income of urban farmers has increased by 15% annually due to diversified revenue streams.
- Urban farming projects have received over $100 million in private investment in the past decade.
- The adoption of urban farming practices has led to a 10% increase in property values in surrounding areas.
- Urban farms have been instrumental in reducing the urban food gap, with a 30% increase in fresh produce availability in low-income neighborhoods.
- The USDA has allocated $5 million annually for urban farming research and development initiatives.
- Urban farms have been found to support pollinator populations, with a 25% increase in urban bee colonies reported.
- Approximately 40% of urban farms are involved in some form of agro-tourism, attracting over 1 million visitors annually.
Benefits of Urban Agriculture
- Reduction of Carbon Emission: Urban farming plays a crucial role in restraining carbon emissions in cities by minimizing fossil fuel consumption that is linked to the vegetables and fruits transportation, packing, and distribution.
- Environmental Sustainability: Using vacant lots, rooftops, balconies, and vertical spaces enhances land use effectiveness in densely populated urban areas and promotes nature and its sustainability.
- Circular Economy: Urban farming assists in managing organic waste by composting eatable scraps and utilizing them as nutrient-rich soil alteration, orienting with circular economy principles and decreasing landfill waste.
- Green Infrastructure and Urban Beautification: The introduction of green spaces, rooftop gardens, vertical farms, and urban farming increases the beauty of the city and promotes green infrastructure and urban beautification.
- Food Security and Access: Growing local food through urban farming gives people with less access to grocery stores access to fresh and nutritious produce, addressing food security concerns.
- Economic Benefits: Urban farming creates job opportunities, supports small-budget businesses, and braces the local economy through the farmer’s market farm to able initiatives and also agri-tourism.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Urban farming mitigates climate change by isolating carbon dioxide from plant growth and soil management practices.
- Urban Revitalization: By transforming the vacant lots into productive spaces and initiating irregular gardening beautifying the urban areas.
Vertical Farming Industry Statistics
- New York City-based indoor vertical agriculture company “Bowery” has been valued at $172.5 million in private funding.
- Within five years, 56% of vertical farmers report positive ROI within 5 years.
- As per urban farming statistics, vertical agriculture emits almost 70% less carbon than traditional farming.
- Singapore has over 139 rooftop farms in Asia.
- By 2024, the vertical agriculture market in the United States is predicted to reach $3.9 billion.
- The crop yield has increased by 50% through the usage of LED lights in vertical agriculture.
- From 2020 to 2025, the compound yearly growth rate CAGR is estimated to grow by nearly 21%.
- The worldwide vertical farming market size is almost $2.23 billion.
- The lighting in vertical agriculture accounts for a noteworthy amount: almost 38% of the total operating cost.
- The Hydroponics technique is the most used growth mechanism in the vertical agriculture industry.
- Green leafy vegetables account for almost 57% of the total vegetables produced in vertical farming.
- Vertical farming allows year-round crop production, regardless of how the weather is.
- Vertical farming can produce almost 44,000 pounds of tomatoes on a single acre, compared to traditional farming’s 10,000 pounds.
- By 2026, the European vertical farming market is predicted to reach $2 billion.
- Vertical farms can be 400 times more productive per square foot than normal outdoor farming.
- Indoor farming uses almost 95% less water, so it’s more affordable.
- The worldwide market for vertical farming is estimated to reach over $12 billion by 2026.
Agricultural Technologies Trends
- Precision Agriculture: The use of innovative technologies like drones, satellites, and Internet of Things devices to collect data and implement farming practices leads to increased effectiveness and lower resource waste.
- Vertical Farming: Urban indoor farming allows crop production all year round, reduces transportation costs, and increases local food security.
- Lab Grown Meat: The innovation of cultured meat products to lower environmental impacts and improve animal well-being while addressing a worldwide food demand.
- Automated Farming Equipment: The use of robotics and AI machines for farming tasks like planting, weeding, and harvesting can lower labor costs and increase efficiency.
- Genetic Engineering: The development of genetic technology to increase specific traits in crops and livestock like resistance to infections or improve immunity.
- Farm Management Software: Digital tools for collecting and analyzing farm data enable farmers to optimize their practices for maximum yield and effectiveness.
- Aquaponics And Hydroponics: The use of soil-less systems for cultivating plants, using water and nutrient solutions to lower and minimize resource use and water.
- Microbial Advancements: The development of bio-fertilizers, bio-pesticides, and other microbial innovations that are sustainable options to the traditional chemicals in farming.
- Waste Reduction Technologies: The use of various methods and solutions for the reduction of food waste that also includes better packaging, storage, and processing techniques.
- Farm-to-Table: There has been an increase in demand for local sources of food and produce, which encourages greater farmer-consumer connections and supports local farming sectors.
- Blockchain Technology: The use of blockchain in the supply chain enables data transparency and helps to ensure food safety.
- Agri-Drones: The use of drones to keep a watch on crop health, apply fertilizers and pesticides, and also accumulate data for good decision-making in farming.
- Internet-on-Things: The integration of sensors, cameras, and other connected devices to collect real-time data and improve precision farming practices.
- Indoor Farming techniques: The innovation and adaption of LED lighting, AI-driven climate control system, and data analytics for indoor crop growth.
- Urban Agriculture: The promotion and the growth of farming in the cities that are improving local food systems and reducing the environmental impact associated with transport and farming land use.
Successful Examples of Urban Farming
- Parisian Mushrooms (Paris, France): Reviving the cultivation of the “champignon de Paris” mushroom variety in organic farms near Paris, continuing a tradition that dates back to the 17th century.
- Sharing Backyards (Canada, U.S., New Zealand): A platform that connects people who want to grow their food but lack space with those who have unused yards. This initiative promotes community gardening and provides support for gardeners.
- Sky Greens (Singapore): Utilizing vertical farming techniques within greenhouses, Sky Greens is the world’s first low-carbon hydraulic water-driven urban vertical farm. It aims to increase local food production efficiency and sustainability in Singapore.
- Urban Roots (Glasgow, UK): Community gardens in Glasgow repurpose vacant industrial land to grow a variety of produce. Volunteers help with cultivation, and the project has been successful in providing fresh vegetables locally.
- GrowUp Urban Farms (London, UK): Combining aquaculture with agriculture in urban settings, GrowUp Urban Farms utilizes aquaponics in an industrial warehouse in London. This closed-loop system produces fish, salads, and herbs with low energy and water usage.
These initiatives demonstrate the diverse approaches to urban agriculture, ranging from traditional methods revived with modern practices to innovative technologies like aquaponics and vertical farming. They address the need for sustainable food production, community engagement, and utilizing underutilized urban spaces for agriculture
Conclusion
Urban farming has been growing in popularity. It is an essential form of farming that has the potential to contribute a notable portion of global vegetable production, generate job opportunities, reduce water consumption and fertilizer use, lower urban temperatures, and feed millions of populations.
The urban farming statistics presented in this blog post demonstrate the impressive reach of urban agriculture all around the world, from providing almost 10% of the worldwide vegetable production to supplying almost 200,000 people with food. With many advantages for both individuals and cities alike, it’s clear that urban agriculture will continue to grow as a viable option for sustainable agricultural practice globally.

